Customers Mail CloudのWebhookは2種類あります。
- メール受信時
- メール送信時
メール送信時は、送信したメールに対してステータスが変わったタイミングで通知が送られるものです。
その際、 application/json を指定しない設定ができます。この時のデータがどうなっているのか紹介します。
<!—more—>
AWS Lambdaの準備
AWS Lambdaで新しい関数を作成します。その際、条件として以下を指定します。
- ランタイム
Java 21 - 関数 URL を有効化
チェックを入れる - 認証タイプ
NONE
関数の作成が完了したら、関数コードを編集します。ベースになるコードは以下の通りです。
package com.example.lambda; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.RequestHandler; import java.util.Map; public class HelloLambda implements RequestHandler<Map<String, Object>, String> { @Override public String handleRequest(Map<String, Object> event, Context context) { return "OK"; } }
受け取るWebhookの設定
管理画面にて、受け取るWebhookを設定できます。設定は以下が用意されています。
- Bounces
- bounced(エラーメールを受け取る)
- Deliveries
- queued(キューに入ったタイミング)
- succeeded(送信完了)
- failed(送信失敗)
- deferred(送信延期)
この中で application/json を指定できます。指定しなかった場合、データは application/x-www-form-urlencoded にて送信されます。本記事ではこの場合を想定しています。
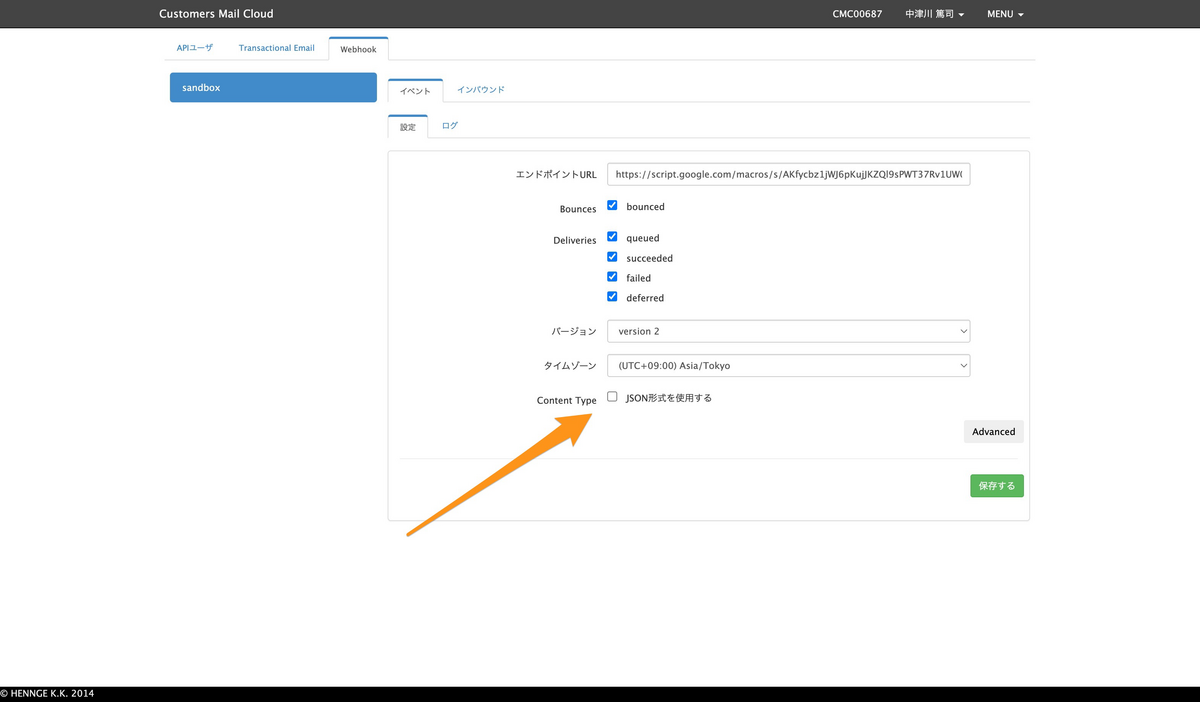
送信されてくるデータについて
メール送信した直後
メール送信を行うと、そのデータがキューに入ります。そして、以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます(データは一部マスキングしています)。データは分かりやすいようにJSONにしていますが、実際には異なりますので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"100.100.100.1","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"","status":"queued"}]}' }
メール送信完了時
Customers Mail Cloudからメール送信処理が行われると、ステータスが succeeded になったWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:09","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"succeeded"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(メールアドレス形式に問題がある場合)
メールアドレスの形式に問題があるなど、送信処理が失敗した場合には以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"host unknown","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:05:15","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<8f902ee7-ae65-8711-48a8-2f708cb14205@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example","status":"1"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってくる場合)
ユーザーが存在しない、メールボックスがいっぱいなど送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってきた場合には、以下のようなJSONが返ってきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"failed"}]}' }
エラーとしてのWebhookも送られてきます。上記のものと event_type が異なるので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:07","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","status":"2"}]}' }
Javaのコード
処理は src/main/java/com/example/lambda/HelloLambda.java に記述します。
package com.example.lambda; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.RequestHandler; import java.util.Map; public class HelloLambda implements RequestHandler<Map<String, Object>, String> { @Override public String handleRequest(Map<String, Object> event, Context context) { return "OK"; } }
また、データの入力を格納するクラスを用意します。 src/main/java/com/example/lambda/Input.java に記述します。クラスのプロパティはCustomers Mail Cloudのドキュメントを参考にしています。
package com.example.lambda; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; import java.util.List; @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class Input { public String eventType; public String serverComposition; public Event event; public static class Event { public List<MessageEvent> deliveries; public List<MessageEvent> bounces; } public static class MessageEvent { public String reason; public String sourceIp; public String returnPath; public String created; public String subject; public String apiData; public String messageId; public String from; public String to; public String senderIp; public String status; } }
全体の流れ
処理の流れは以下の通りです。
- Base64エンコードされたボディをデコード
- URLエンコードされたフォームデータをパース
- 単純なフィールドを直接取得
- JSONフィールドはJacksonでオブジェクト化
- ログ出力
Base64エンコードされたボディをデコード
API Gateway を通じて Lambda に渡される時、body はBase64エンコードされています。そのため、まずはデコードして元の文字列に戻します。
// リクエストボディ(Base64エンコードされた文字列)を取得 String encodedBody = (String) event.get("body"); // Base64デコードしてバイト配列に戻す byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encodedBody); // バイト配列をUTF-8文字列に変換 String formBody = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
URLエンコードされたフォームデータをパース
次に、URLエンコードされたフォームデータをパースします。Javaでは java.net.URLDecoder を使ってデコードできます。
// フォームデータを key-value 形式に変換(例:event_type=xxx&event=yyy)
Map<String, String> formMap = parseForm(formBody);
parseForm メソッドは以下のように実装します。この関数では、URLエンコードされた文字列を & で分割し、各部分を = で分けてMapに格納します。
// URLエンコードされたフォームデータを key-value 形式のMapに変換するメソッド private Map<String, String> parseForm(String body) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); // フォームデータは "key1=value1&key2=value2" という形式 // & で分割し、1つずつ key=value に分解する for (String pair : body.split("&")) { String[] parts = pair.split("=", 2); // key をデコード(URLエンコードされている可能性があるため) String key = URLDecoder.decode(parts[0], StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // value もデコード、値がない場合は空文字を入れる String value = parts.length > 1 ? URLDecoder.decode(parts[1], StandardCharsets.UTF_8) : ""; // key と value をMapに格納 map.put(key, value); } // 完成したMapを返す return map; }
単純なフィールドを直接取得
次に、単純なフィールド( event_type や server_composition )は直接取得して、Javaオブジェクトに格納します。 event フィールドはJSON形式なので、Jacksonを使ってJavaオブジェクトに変換します。
// JSONをJavaオブジェクトに変換するためのツールを準備 ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 入力データを格納するクラスのインスタンスを作成 Input input = new Input(); // フォームデータから event_type を取得して設定 input.eventType = formMap.get("event_type"); // フォームデータから server_composition を取得して設定 input.serverComposition = formMap.get("server_composition"); // event フィールドは JSON 形式なので、Javaオブジェクトに変換して格納 String eventJson = formMap.get("event"); if (eventJson != null) { input.event = mapper.readValue(eventJson, Input.Event.class); }
ログ出力
今回は、最後にデバッグ用にログ出力を行います。 System.out.println を使って、各フィールドの値を表示します。
// デバッグ用にパースした結果を出力 System.out.println("Parsed input:"); System.out.println("event_type: " + input.eventType); System.out.println("server_composition: " + input.serverComposition); // event の中に deliveries(配信情報)があれば1件ずつ出力 if (input.event != null && input.event.deliveries != null) { for (Input.MessageEvent msg : input.event.deliveries) { System.out.println("Delivery: " + msg.subject + " → " + msg.to + " [" + msg.status + "]"); } }
出力例は以下の通りです。
Parsed input: event_type: deliveries server_composition: pro Delivery: メールマガジンのテスト → user@smtps.jp [queued]
全体のコード
// HelloLambda.java package com.example.lambda; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context; import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.RequestHandler; import java.util.Base64; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.net.URLDecoder; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; public class HelloLambda implements RequestHandler<Map<String, Object>, String> { @Override public String handleRequest(Map<String, Object> event, Context context) { try { String encodedBody = (String) event.get("body"); byte[] decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(encodedBody); String formBody = new String(decodedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // フォームを key-value にパース Map<String, String> formMap = parseForm(formBody); ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); Input input = new Input(); // 単純フィールドを直接マッピング input.eventType = formMap.get("event_type"); input.serverComposition = formMap.get("server_composition"); // event フィールドだけ JSONとしてパース String eventJson = formMap.get("event"); if (eventJson != null) { input.event = mapper.readValue(eventJson, Input.Event.class); } // デバッグ出力 System.out.println("Parsed input:"); System.out.println("event_type: " + input.eventType); System.out.println("server_composition: " + input.serverComposition); if (input.event != null && input.event.deliveries != null) { for (Input.MessageEvent msg : input.event.deliveries) { System.out.println("Delivery: " + msg.subject + " → " + msg.to + " [" + msg.status + "]"); } } return "OK"; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "ERROR"; } } private Map<String, String> parseForm(String body) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); for (String pair : body.split("&")) { String[] parts = pair.split("=", 2); String key = URLDecoder.decode(parts[0], StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String value = parts.length > 1 ? URLDecoder.decode(parts[1], StandardCharsets.UTF_8) : ""; map.put(key, value); } return map; } } // Input.java package com.example.lambda; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; import java.util.List; @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class Input { public String eventType; public String serverComposition; public Event event; public static class Event { public List<MessageEvent> deliveries; public List<MessageEvent> bounces; } public static class MessageEvent { public String reason; public String sourceIp; public String returnPath; public String created; public String subject; public String apiData; public String messageId; public String from; public String to; public String senderIp; public String status; } }
まとめ
Webhookを使うことで、メール送信ステータスの変化に応じて通知を受け取れるようになります。メールと連携したシステムを開発する際に役立つでしょう。
AWS Lambdaの場合は application/json を指定した方が全体として、受け取りやすい印象です。ぜひお試しください。なお、このWebhookはSMTP経由の場合、利用できます。
