Customers Mail CloudのWebhookは2種類あります。
- メール受信時
- メール送信時
メール送信時は、送信したメールに対してステータスが変わったタイミングで通知が送られるものです。
その際、 application/json を指定しない設定ができます。この時のデータがどうなっているのか紹介します。
<!—more—>
Google Cloud Functionsの準備
今回はローカルで開発する流れを紹介します。まず、適当なフォルダを作成します。今回はcmcとします。
mkdir cmc cd cmc
そして Gemfile というファイルを作成し、以下のように記述します。
# frozen_string_literal: true source "https://rubygems.org" # gem "rails" gem "functions_framework"
そしてライブラリをインストールします。
bundle install
次に app.rb というファイルを作成します。以下は空の内容ですが、後で処理を記述します。
#== app.rb ==# require "functions_framework" require "json" FunctionsFramework.http "cmc" do |req| # この中に処理を記述します "Hello, Customers Mail Cloud!" end
そして、以下のようにコマンドを実行します。
bundle exec functions-framework-ruby --source=app.rb --target=cmc
これで http://localhost:8080 でサーバーが立ち上がります。
受け取るWebhookの設定
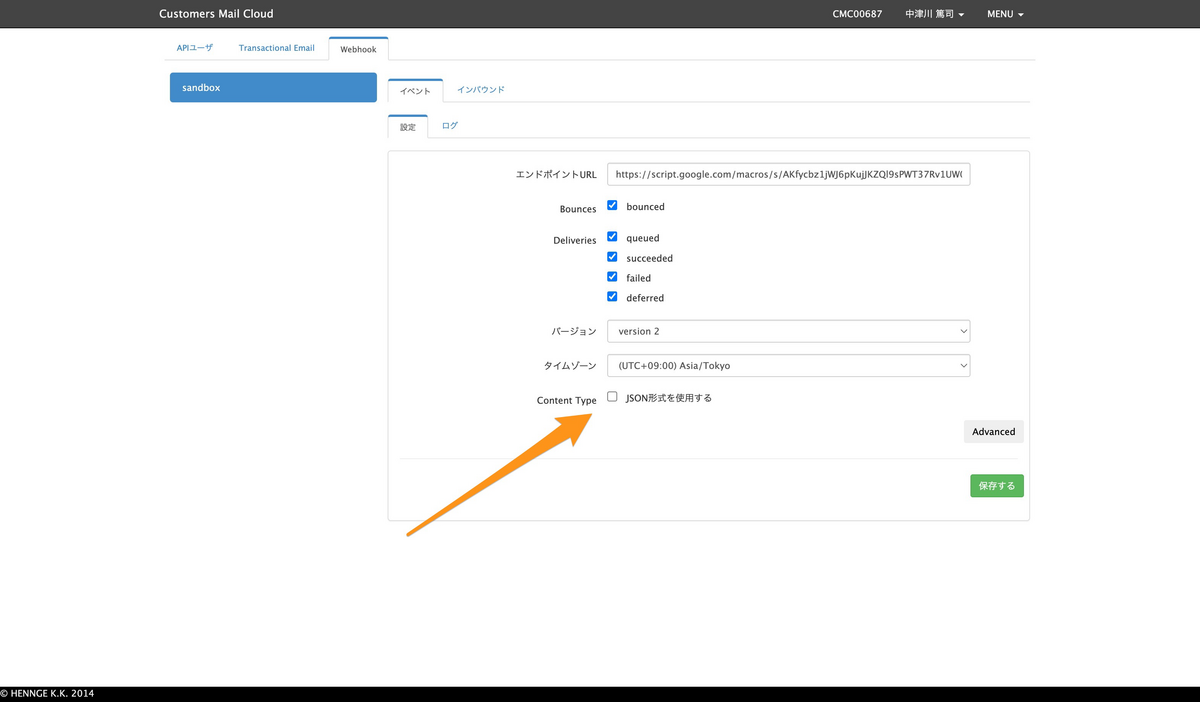
管理画面にて、受け取るWebhookを設定できます。設定は以下が用意されています。
- Bounces
- bounced(エラーメールを受け取る)
- Deliveries
- queued(キューに入ったタイミング)
- succeeded(送信完了)
- failed(送信失敗)
- deferred(送信延期)
この中で application/json を指定できます。指定しなかった場合、データは application/x-www-form-urlencoded にて送信されます。本記事ではこの場合を想定しています。
送信されてくるデータについて
メール送信した直後
メール送信を行うと、そのデータがキューに入ります。そして、以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます(データは一部マスキングしています)。データは分かりやすいようにJSONにしていますが、実際には異なりますので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"100.100.100.1","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"","status":"queued"}]}' }
メール送信完了時
Customers Mail Cloudからメール送信処理が行われると、ステータスが succeeded になったWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:09","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"succeeded"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(メールアドレス形式に問題がある場合)
メールアドレスの形式に問題があるなど、送信処理が失敗した場合には以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"host unknown","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:05:15","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<8f902ee7-ae65-8711-48a8-2f708cb14205@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example","status":"1"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってくる場合)
ユーザーが存在しない、メールボックスがいっぱいなど送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってきた場合には、以下のようなJSONが返ってきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"failed"}]}' }
エラーとしてのWebhookも送られてきます。上記のものと event_type が異なるので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:07","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","status":"2"}]}' }
Rubyのコード
処理は app.rb の FunctionsFramework.http ブロック内に記述します。
FunctionsFramework.http "cmc" do |req| # この中に処理を記述します "Hello, Customers Mail Cloud!" end
送られてくるデータは req.params で受け取れます。 req.params[キー] でアクセスできますが、 event キー以下は文字列になっています。そのため、追加で JSON.parse を行って、オブジェクトにします。
puts req.params["event_type"] event = JSON.parse(req.params['event'])
これで event 内にあるデータに対してアクセスできます。
status = event["bounces"] || event["deliveries"]
まとめ
Webhookを使うことで、メール送信ステータスの変化に応じて通知を受け取れるようになります。メールと連携したシステムを開発する際に役立つでしょう。
Rubyの場合は application/json を指定した方が全体として、受け取りやすい印象です。ぜひお試しください。なお、このWebhookはSMTP経由の場合、利用できます。
