Customers Mail CloudのWebhookは2種類あります。
- メール受信時
- メール送信時
メール送信時は、送信したメールに対してステータスが変わったタイミングで通知が送られるものです。
本記事では実際にどういった内容が送られてくるのかを紹介します。
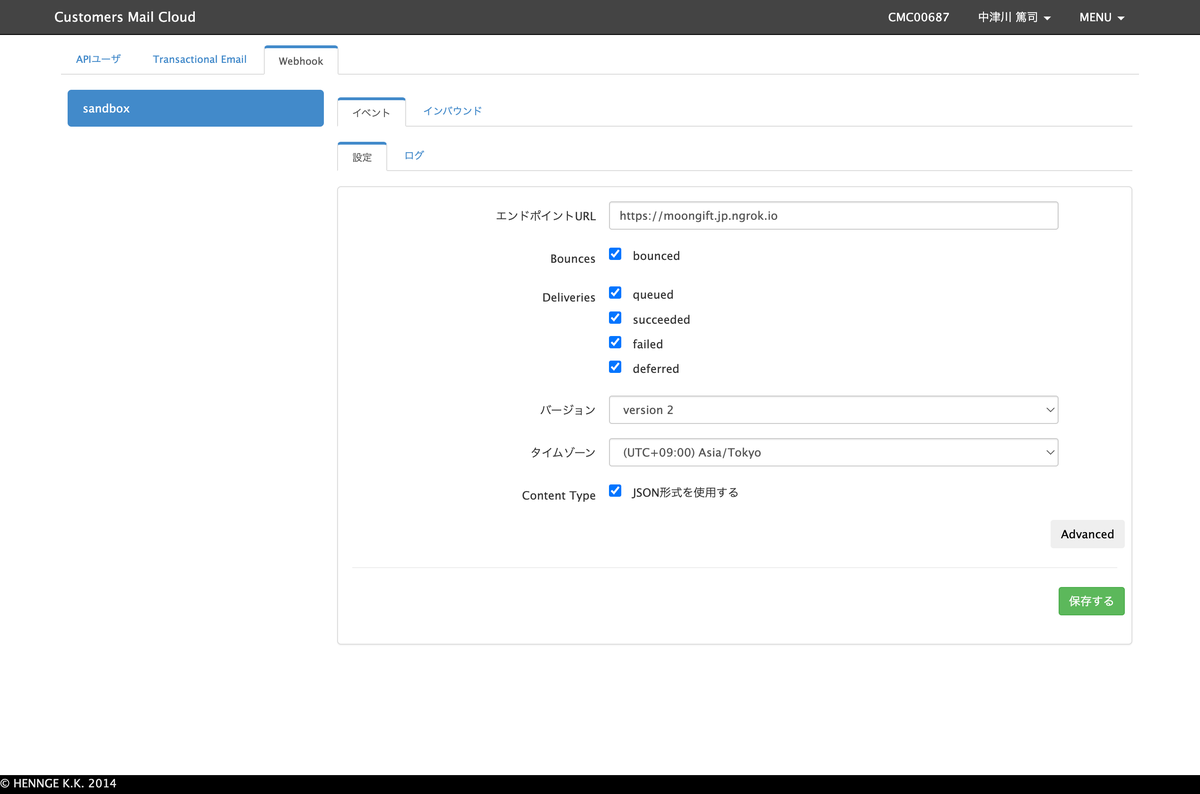
受け取るWebhookの設定
管理画面にて、受け取るWebhookを設定できます。設定は以下が用意されています。
- Bounces
- bounced(エラーメールを受け取る)
- Deliveries
- queued(キューに入ったタイミング)
- succeeded(送信完了)
- failed(送信失敗)
- deferred(送信延期)
送信されてくるデータについて
メール送信した直後
メール送信を行うと、そのデータがキューに入ります。そして、以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます(データは一部マスキングしています)。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": { "deliveries": [ { "reason": "", "sourceIp": "100.100.100.1", "returnPath": "info@return.pro.smtps.jp", "created": "2023-01-25 14:03:06", "subject": "メールマガジンのテスト", "apiData": "", "messageId": "<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>", "from": "info@example.com", "to": "user@example.jp", "senderIp": "", "status": "queued" } ] } }
メール送信完了時
Customers Mail Cloudからメール送信処理が行われると、ステータスが succeeded になったWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": { "deliveries": [ { "reason": "", "sourceIp": "", "returnPath": "info@return.pro.smtps.jp", "created": "2023-01-25 14:03:09", "subject": "メールマガジンのテスト", "apiData": "", "messageId": "<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>", "from": "info@example.com", "to": "user@example.jp", "senderIp": "100.100.100.3", "status": "succeeded" } ] } }
メール送信失敗時(メールアドレス形式に問題がある場合)
メールアドレスの形式に問題があるなど、送信処理が失敗した場合には以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": { "bounces": [ { "reason": "host unknown", "returnPath": "info@return.pro.smtps.jp", "created": "2023-01-25 14:05:15", "subject": "メールマガジンのテスト", "apiData": "", "messageId": "<8f902ee7-ae65-8711-48a8-2f708cb14205@example.com>", "from": "info@example.com", "to": "user@example", "status": "1" } ] } }
メール送信失敗時(送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってくる場合)
ユーザーが存在しない、メールボックスがいっぱいなど送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってきた場合には、以下のようなJSONが返ってきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": { "deliveries": [ { "reason": "550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)", "sourceIp": "", "returnPath": "info@return.pro.smtps.jp", "created": "2023-01-25 14:06:06", "subject": "メールマガジンのテスト", "apiData": "", "messageId": "<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>", "from": "info@example.com", "to": "no-user@example.jp", "senderIp": "100.100.100.3", "status": "failed" } ] } }
エラーとしてのWebhookも送られてきます。上記のものと event_type が異なるので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": { "bounces": [ { "reason": "550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)", "returnPath": "info@return.pro.smtps.jp", "created": "2023-01-25 14:06:07", "subject": "メールマガジンのテスト", "apiData": "", "messageId": "<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>", "from": "info@example.com", "to": "no-user@example.jp", "status": "2" } ] } }
Google Cloud Functionsの準備
今回はローカルで開発する流れを紹介します。まずFunction.csというファイルを作成し、内容を以下のように記述します。
using Google.Cloud.Functions.Framework;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System;
using System.IO;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace HelloWorld;
public class Function : IHttpFunction
{
public async Task HandleAsync(HttpContext context)
{
// この中に処理を記述します
await context.Response.WriteAsync("ok");
}
}
次に、 HelloWorld.csproj というファイルを作成し、以下のように記述します。
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk"> <PropertyGroup> <OutputType>Exe</OutputType> <TargetFramework>net6.0</TargetFramework> </PropertyGroup> <ItemGroup> <PackageReference Include="Google.Cloud.Functions.Hosting" Version="2.1.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Newtonsoft.Json" Version="13.0.3" /> </ItemGroup> </Project>
これで準備は完了です。関数は以下のように実行します。
dotnet run
実行すると、 http://127.0.0.1:8080 でサーバーが立ち上がります。
クラスの定義
Webhookで送られてくるデータに合わせて、クラスを定義します。
namespace HelloWorld;
public class Email
{
public string event_type { get; set; }
public string server_composition { get; set; }
public Event @event { get; set; }
}
上記クラス内で利用している Event クラスは以下のように定義します。
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HelloWorld;
public class Event
{
public List<EventType> bounces { get; set; }
public List<EventType> deliveries { get; set; }
public List<EventType> blocks { get; set; }
}
最後にEventクラス内で使われている EventType クラスです。
namespace HelloWorld;
public class EventType
{
public string reason { get; set; }
public string returnPath { get; set; }
public string created { get; set; }
public string subject { get; set; }
public string apiData { get; set; }
public string messageId { get; set; }
public string from { get; set; }
public string to { get; set; }
public string status { get; set; }
}
POSTを受け取った際の処理
context.Request.Body にPOSTデータが入っていますので、そのデータを読み込んで JsonConvert.DeserializeObject によってデシリアライズします。
var sr = new StreamReader(context.Request.Body); var email = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Email>(await sr.ReadToEndAsync());
これで email は Email クラスのインスタンスとして利用できます。
Console.WriteLine(email.event_type); Console.WriteLine(email.@event.bounces[0].reason);
全体のコード
全体のコードは以下のようになります。
using Google.Cloud.Functions.Framework;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System;
using System.IO;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace HelloWorld;
public class Function : IHttpFunction
{
public async Task HandleAsync(HttpContext context)
{
var sr = new StreamReader(context.Request.Body);
var email = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Email>(await sr.ReadToEndAsync());
Console.WriteLine(email.event_type);
Console.WriteLine(email.@event.bounces[0].reason);
await context.Response.WriteAsync("ok");
}
}
まとめ
Webhookを使うことで、メール送信ステータスの変化に応じて通知を受け取れるようになります。メールと連携したシステムを開発する際に役立つでしょう。
このWebhookはSMTP経由の場合、利用できます。ぜひご利用ください。
