Customers Mail CloudのWebhookは2種類あります。
- メール受信時
- メール送信時
メール送信時は、送信したメールに対してステータスが変わったタイミングで通知が送られるものです。
その際、 application/json を指定しない設定ができます。この時のデータがどうなっているのか紹介します。
<!—more—>
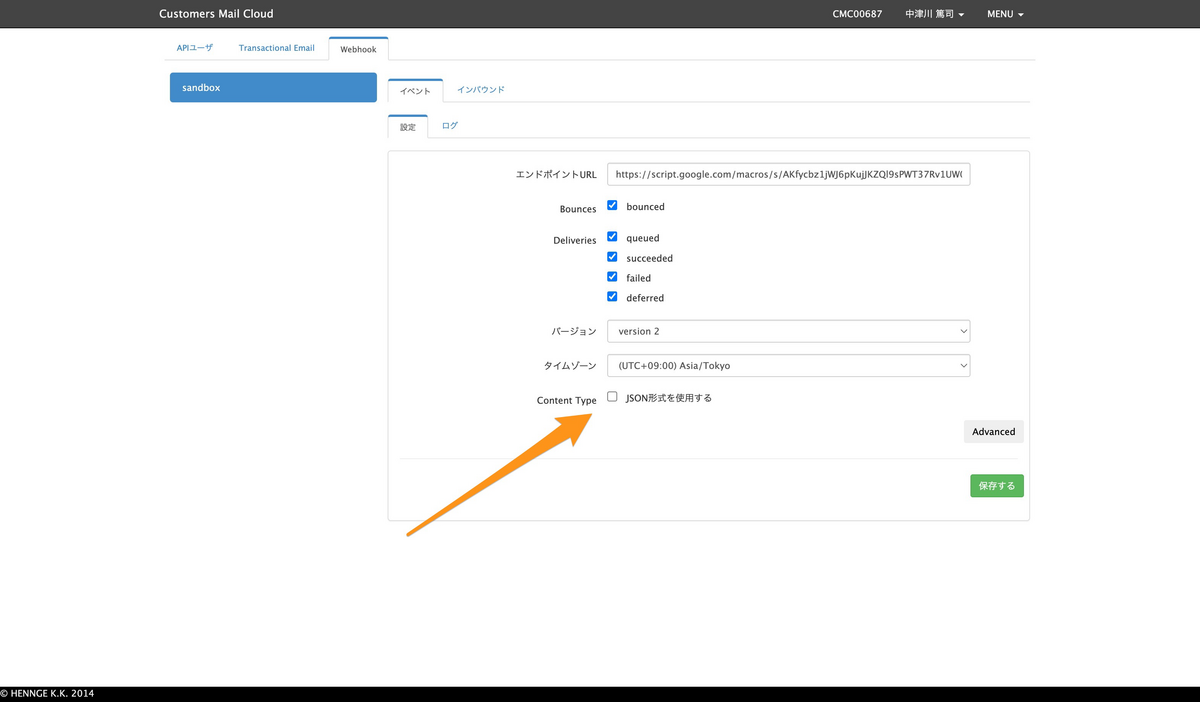
受け取るWebhookの設定
管理画面にて、受け取るWebhookを設定できます。設定は以下が用意されています。
- Bounces
- bounced(エラーメールを受け取る)
- Deliveries
- queued(キューに入ったタイミング)
- succeeded(送信完了)
- failed(送信失敗)
- deferred(送信延期)
この中で application/json を指定できます。この場合、データは **multipart/form-data にて送信されます。本記事ではこの場合を想定しています。
Go言語による実装
Go言語では以下のように作成します。今回はWebフレームワークとしてginを利用しています。まず、プロジェクトを作ります。
go mod init smtps/webhook
また、ginをインストールします。
go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
ginを使った場合のコードは、外観として以下のようになります。今回は POST /mails にてWebhookを受け取る前提になります。最後に必ずHTTPステータス200を返してください。
package main import ( "fmt" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" ) func main() { r := gin.Default() r.POST("/mails", func(c *gin.Context) { // この中で処理します c.JSON(200, gin.H{}) }) r.Run() // 0.0.0.0:8080 でサーバーを立てます。 }
送信されてくるデータについて
メール送信した直後
メール送信を行うと、そのデータがキューに入ります。そして、以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます(データは一部マスキングしています)。データは分かりやすいようにJSONにしていますが、実際には異なりますので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"100.100.100.1","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"","status":"queued"}]}' }
メール送信完了時
Customers Mail Cloudからメール送信処理が行われると、ステータスが succeeded になったWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:03:09","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<031a32d4-06cd-b1ae-9526-011c0b9f1296@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"succeeded"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(メールアドレス形式に問題がある場合)
メールアドレスの形式に問題があるなど、送信処理が失敗した場合には以下のようなWebhookが送られてきます。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"host unknown","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:05:15","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<8f902ee7-ae65-8711-48a8-2f708cb14205@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"user@example","status":"1"}]}' }
メール送信失敗時(送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってくる場合)
ユーザーが存在しない、メールボックスがいっぱいなど送信先サーバーからエラーが返ってきた場合には、以下のようなJSONが返ってきます。
{ "event_type": "deliveries", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"deliveries":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","sourceIp":"","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:06","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","senderIp":"100.100.100.3","status":"failed"}]}' }
エラーとしてのWebhookも送られてきます。上記のものと event_type が異なるので注意してください。
{ "event_type": "bounces", "server_composition": "pro", "event": '{"bounces":[{"reason":"550 5.1.1 The email account that you tried to reach does not exist. Please try 5.1.1 double-checking the recipient's email address for typos or 5.1.1 unnecessary spaces. Learn more at 5.1.1 <https://support.google.com/mail/?p=NoSuchUser> b197-20020a621bce000000b0058b80756b07si311029pfb.3 - gsmtp (in reply to RCPT TO)","returnPath":"info@return.pro.smtps.jp","created":"2023-01-25 14:06:07","subject":"メールマガジンのテスト","apiData":"","messageId":"<9e7e564c-ac83-8cd8-2cb4-b9ff2a9f168d@example.com>","from":"info@example.com","to":"no-user@example.jp","status":"2"}]}' }
構造体の作成
**multipart/form-data の場合は基本的に構造体は不要ですが、 event 以下を処理するために構造体を用意しておきます。
type MailEvent struct { Deliveries []MailInfo `json:"deliveries` Bounces []MailInfo `json:"bounces` } type MailInfo struct { Reason string `json:"reason"` ReturnPath string `json:"returnPath"` Created string `json:"created"` Subject string `json:"subject"` ApiData string `json:"apiData"` MessageId string `json:"messageId"` From string `json:"from"` To string `json:"to"` Status string `json:"status"` SourceIp string `json:"sourceIp"` SenderIp string `json:"senderIp"` }
Webhookの処理
例として、以下のように処理を行います。最初に MultipartForm を実行し、multipart/form-dataを想定します。後は c.Request.PostFormでデータが取れますが、値は常に配列なので注意してください。
event 以下は文字列なので、構造体を指定して json.Unmarshal を実行します。
r.POST("/mails", func(c *gin.Context) { c.MultipartForm() for key, value := range c.Request.PostForm { fmt.Printf("%v = %v \n", key, value[0]) } eventStr := c.Request.PostForm["event"][0] event := MailEvent{} if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(eventStr), &event); err == nil { fmt.Println(event.Deliveries[0].SourceIp) } c.JSON(200, gin.H{}) })
まとめ
Webhookを使うことで、メール送信ステータスの変化に応じて通知を受け取れるようになります。メールと連携したシステムを開発する際に役立つでしょう。
Go言語 + ginの場合は application/json を指定した方が全体として、受け取りやすい印象です。ぜひお試しください。なお、このWebhookはSMTP経由の場合、利用できます。
